Matter, Definition, Characteristics, States, Examples, & Facts
5 (649) · € 26.00 · En Stock
Matter, material substance that constitutes the observable universe and, together with energy, forms the basis of all objective phenomena. At the most fundamental level, matter is composed of elementary particles known as quarks and leptons (the class of elementary particles that includes electrons).

Matter - Wikipedia

States of Matter - Definition of Solid, Liquid, Gas & Plasma with Videos of States of Matter

Subatomic particle, Definition, Examples, & Classes

Animalia Kingdom, Definition, Characteristics & Examples - Lesson
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Personally-identifiable-information-pii_final-f413d282a7b74142b147720a77811659.png)
What Is Personally Identifiable Information (PII)? Types and Examples

Atomic Mass, Definition, Characteristics & Examples - Lesson
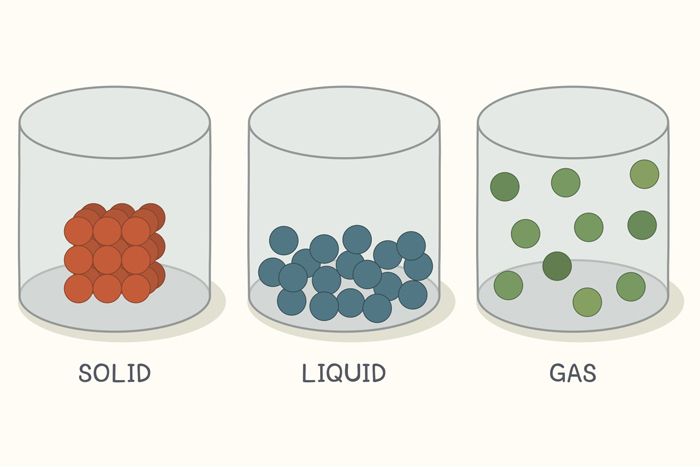
Properties of Matter: Solids

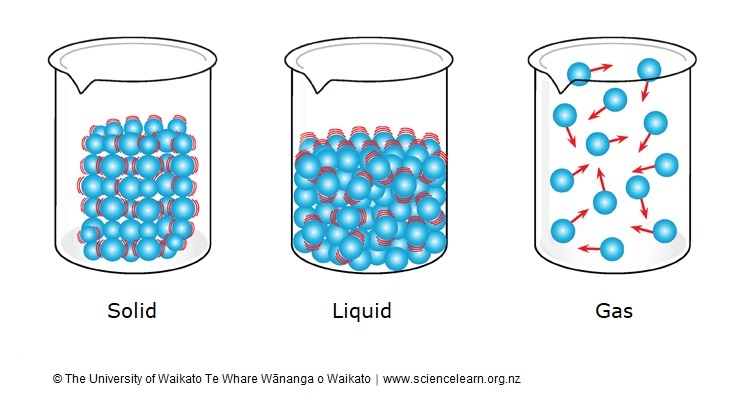
What Is Matter? Definition and Examples
States of Matter: Solids, Liquids, and Gases Study Guide Outline - Characteristics of Matter - King Virtue's Classroom Starting your unit on Matter?
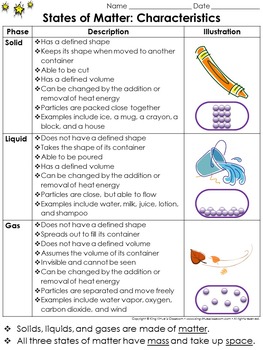
States of Matter: Solids, Liquids, and Gases Study Guide - Characteristics

Talk about three states of matter
Three States of Matter - Definition of Matter, Classification with Videos & Examples of Three States of Matter

matter - Students, Britannica Kids

Matter - Wikipedia
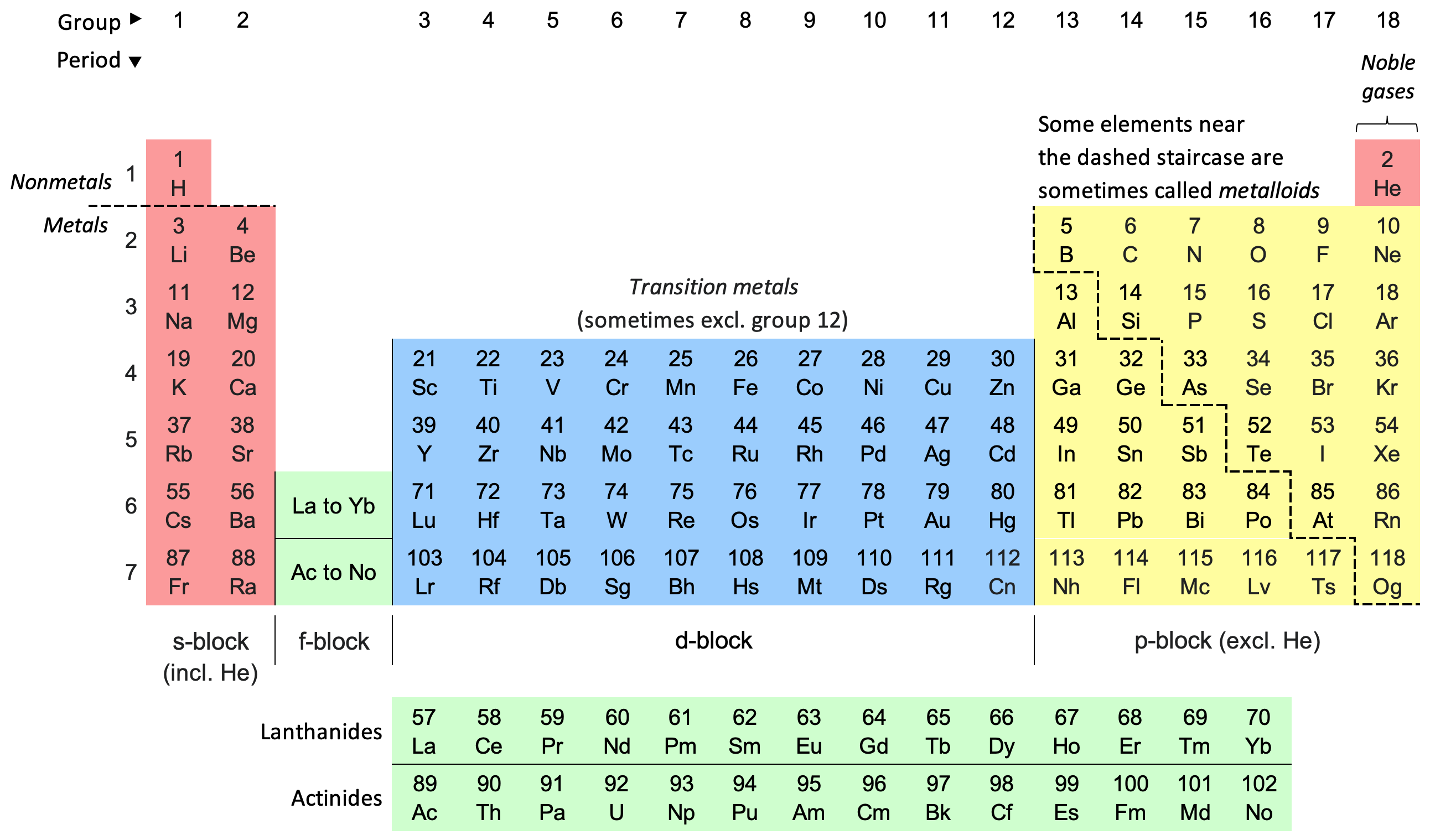
Periodic table - Wikipedia

classification of matter –