Fermentation, Free Full-Text
4.5 (430) · € 19.99 · En Stock
Fermentation technology has a long history and low-temperature fermentation has now become the focus of research. This paper reviews the mechanism and application of low-temperature fermentation and the optimization of relevant strains. Low-temperature fermentation leads to a differential expression of growth in metabolism genes (PSD1, OPI3, ERG3, LCB3 and NTH1). Low-temperature fermentation can be applied to foods and has various advantages, such as increasing changes in volatile flavor compounds and other corresponding metabolic substances of the strain, and inhibited growth of spurious bacteria. The focus of low-temperature fermentation in the long run lies in strain optimization, which is to protect and optimize the strains through a variety of methods. Low-temperature fermentation can greatly improve product quality. At present, the most effective methods to promote low-temperature fermentation are gene knockout and probiotic microencapsulation.

Sandor Katz's Fermentation Journeys - Chelsea Green Publishing
Foam-free production of Surfactin via anaerobic fermentation of

Fermentation and germination improve nutritional value of cereals

Premier Research Labs HM-ND - Features Fermented Chlorella

A New Methodology to Calculate the Ethanol Fermentation Efficiency

Ethanol fermentation - Wikipedia

Our Products

Extracellular electron transfer increases fermentation in lactic
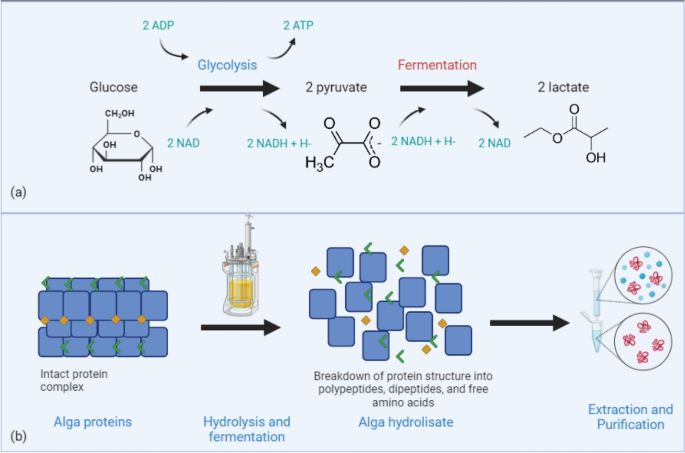
An overview of fermentation in the food industry - looking back
Year of Plenty Set of 12 Fermentation Weights for Use in All Wide

Free eBooks: Making Cultured & Fermented Foods - Cultures For Health
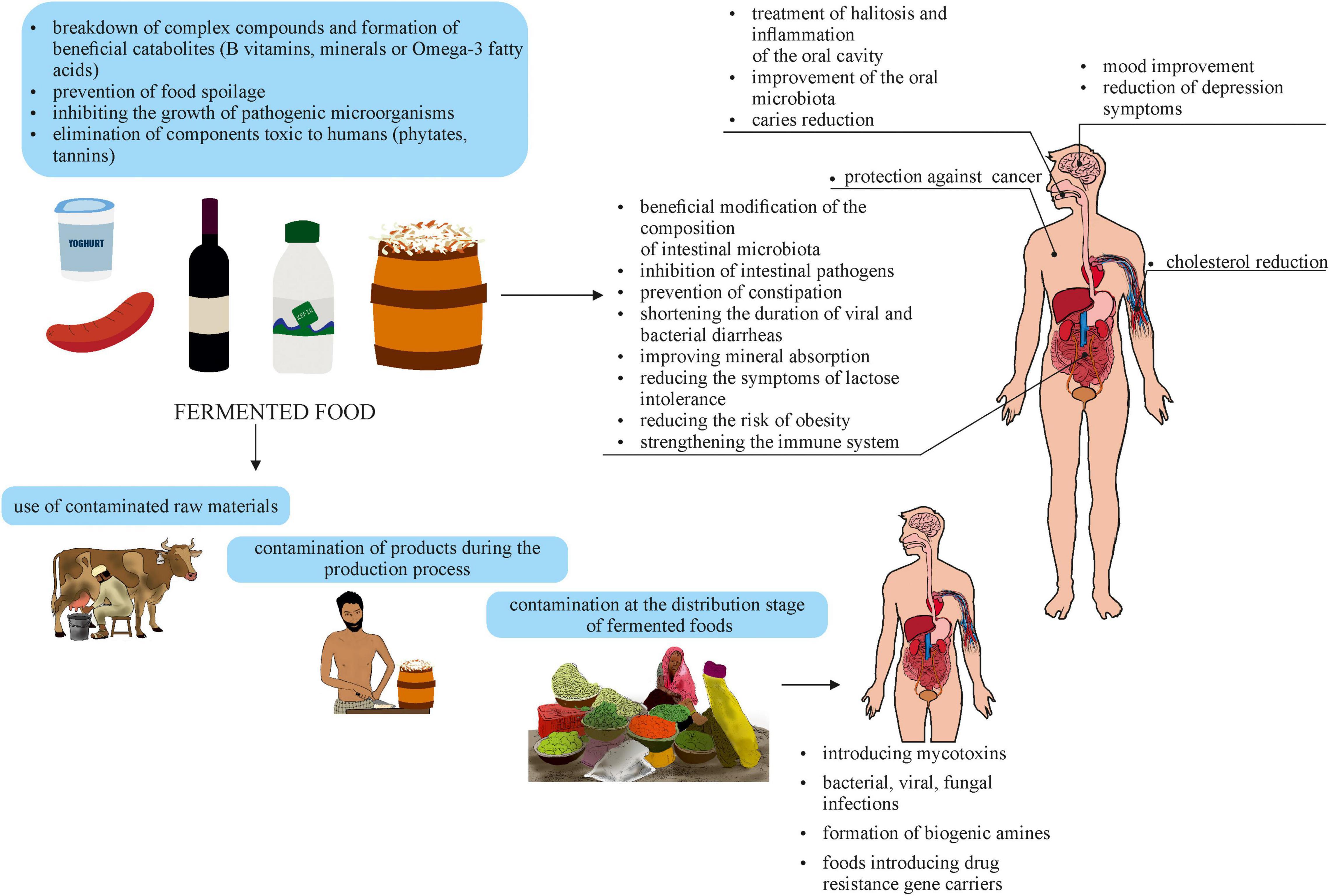
Frontiers Two Faces of Fermented Foods—The Benefits and Threats

Stuck Fermentation: Causes, Prevention and How to Fix Them When
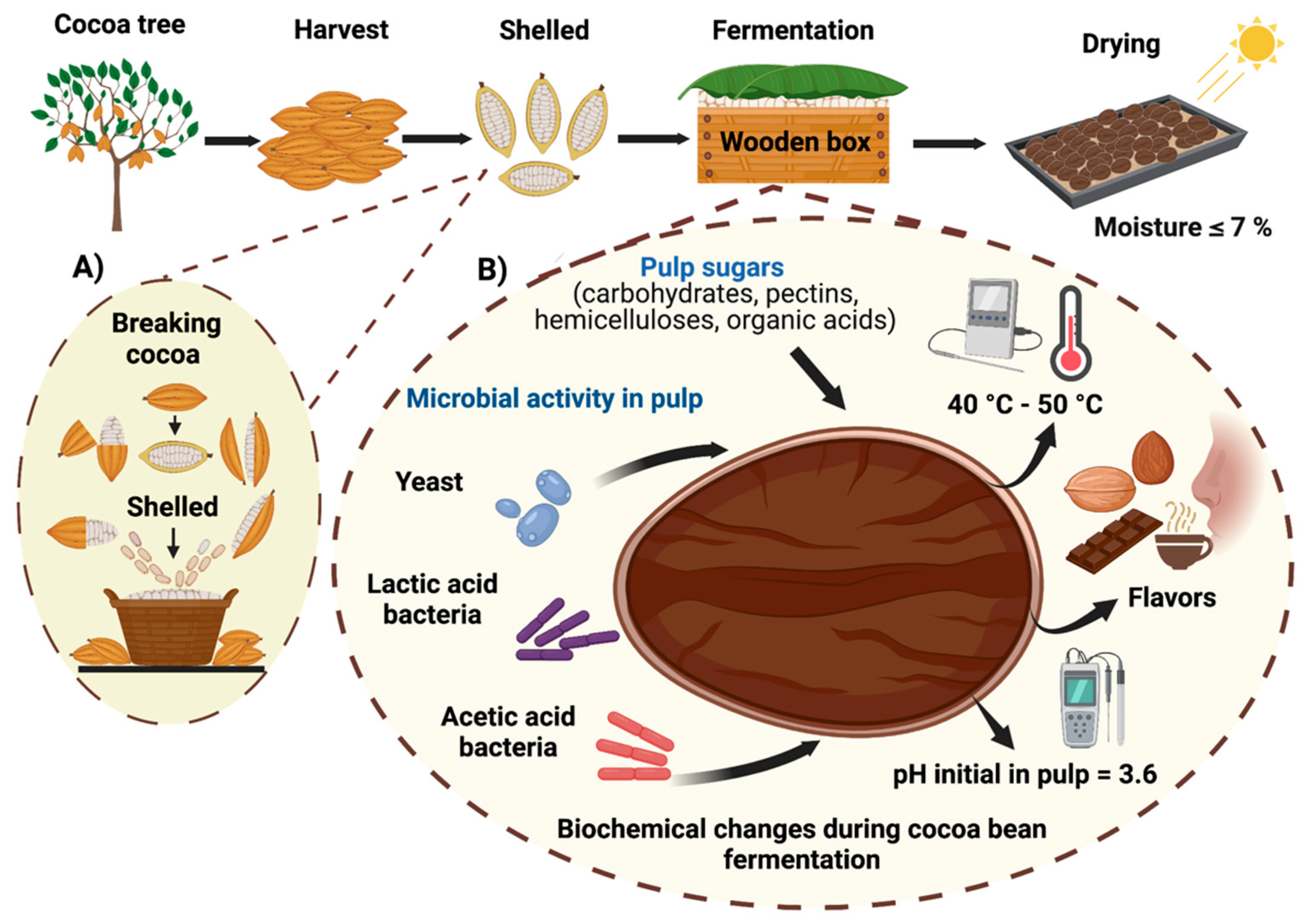
Fermentation, Free Full-Text