Mars: The Planet that Lost an Ocean's Worth of Water
4.8 (640) · € 21.00 · En Stock
A primitive ocean on Mars held more water than Earth’s Arctic Ocean, and covered a greater portion of the planet’s surface than the Atlantic Ocean does on Earth, according to new results published today. An international team of scientists used ESO’s Very Large Telescope, along with instruments at the W. M. Keck Observatory and the NASA Infrared Telescope Facility, to monitor the atmosphere of the planet and map out the properties of the water in different parts of Mars’s atmosphere over a six-year period. These new maps are the first of their kind. The results appear online in the journal Science today.
Will there ever be a time that Mars will have liquid water again and possibly life due to the expansion of the Sun? - Quora
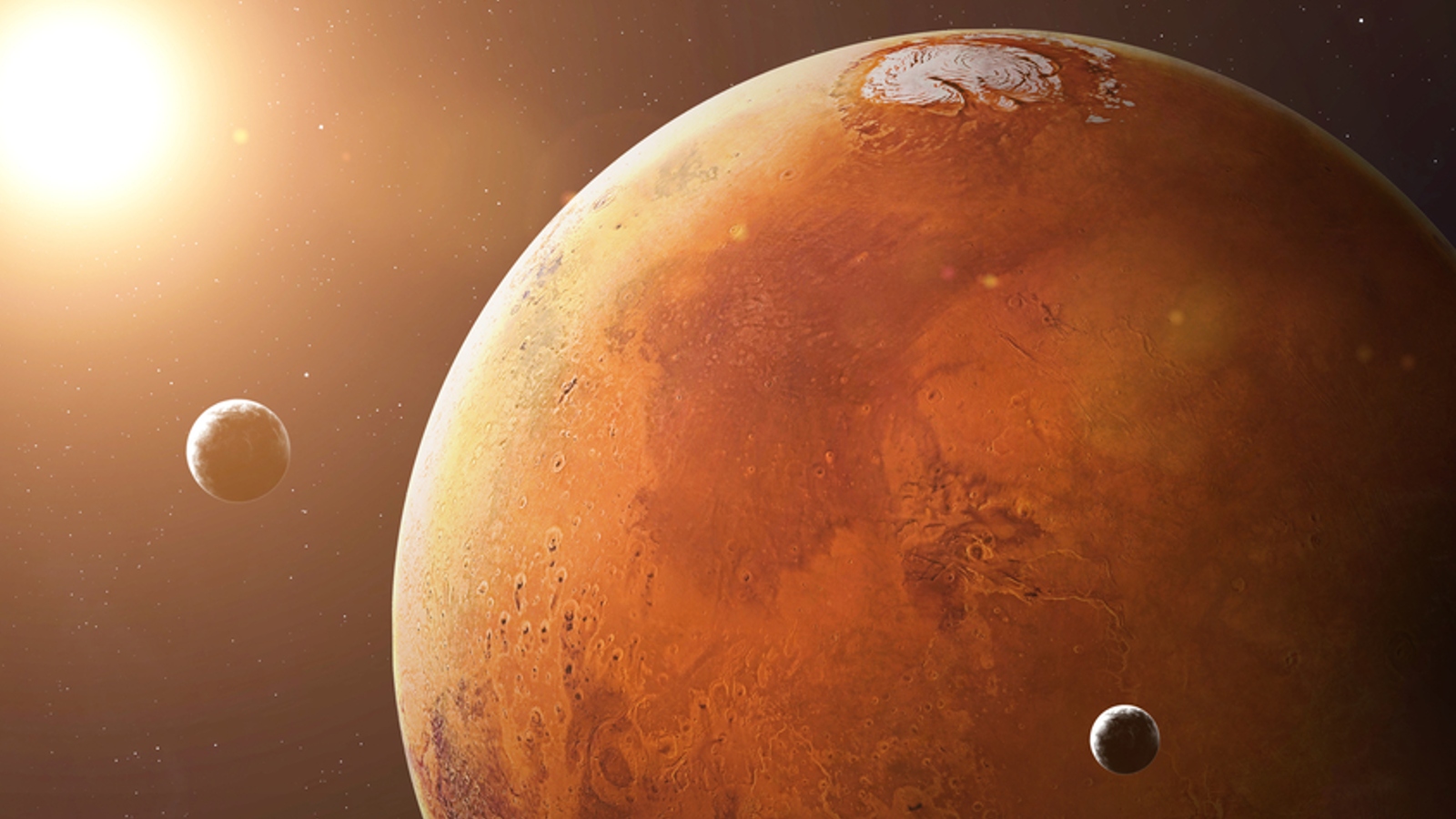

NASA may have unknowingly found and killed alien life on Mars 50 years ago, scientist claims
If Mars had approximately the same percentage of water as Earth, what might it look like? How many continents would it have? - Quora

Mars: The Planet that Lost an Ocean's Worth of Water

Is an Ocean of Mars Water Trapped in the Planet's Crust? - Sky & Telescope - Sky & Telescope

Hubble Spots Possible Evidence of Water on Earth-Sized TRAPPIST-1 Planets

Early meteorites brought enough water to Mars to create a global ocean
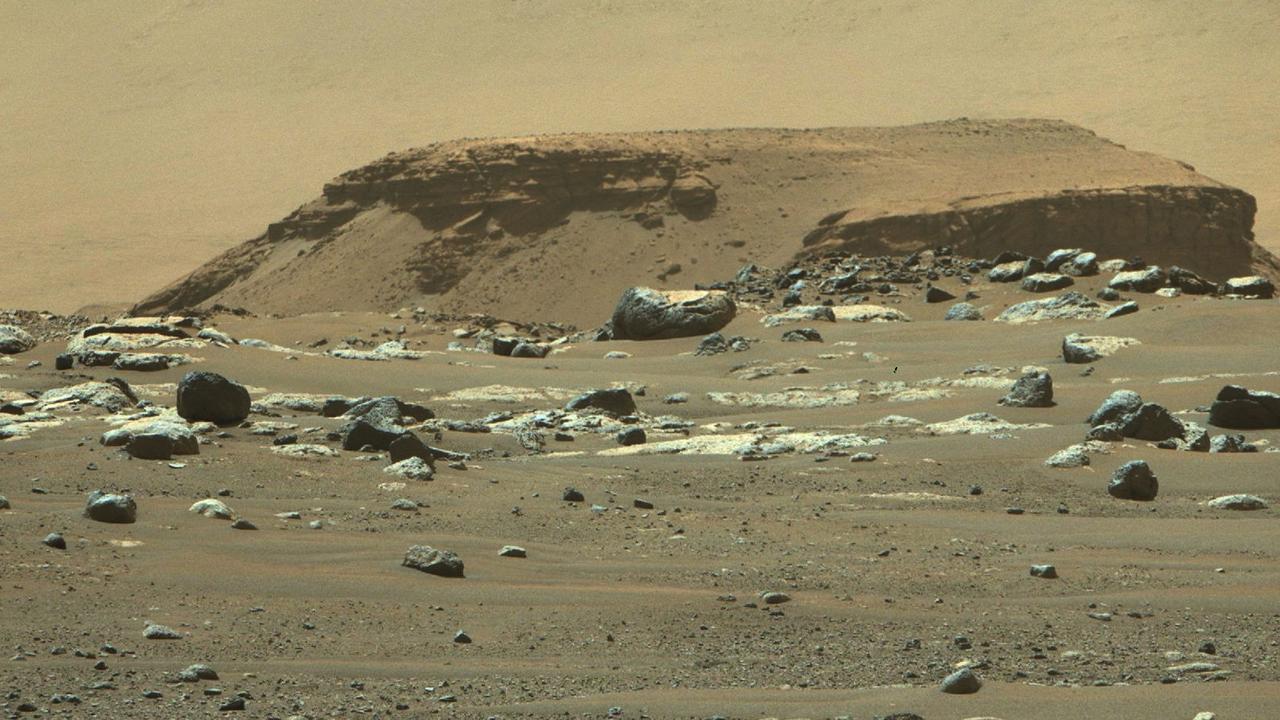

New hypothesis that water on Mars surface was absorbed into its crust
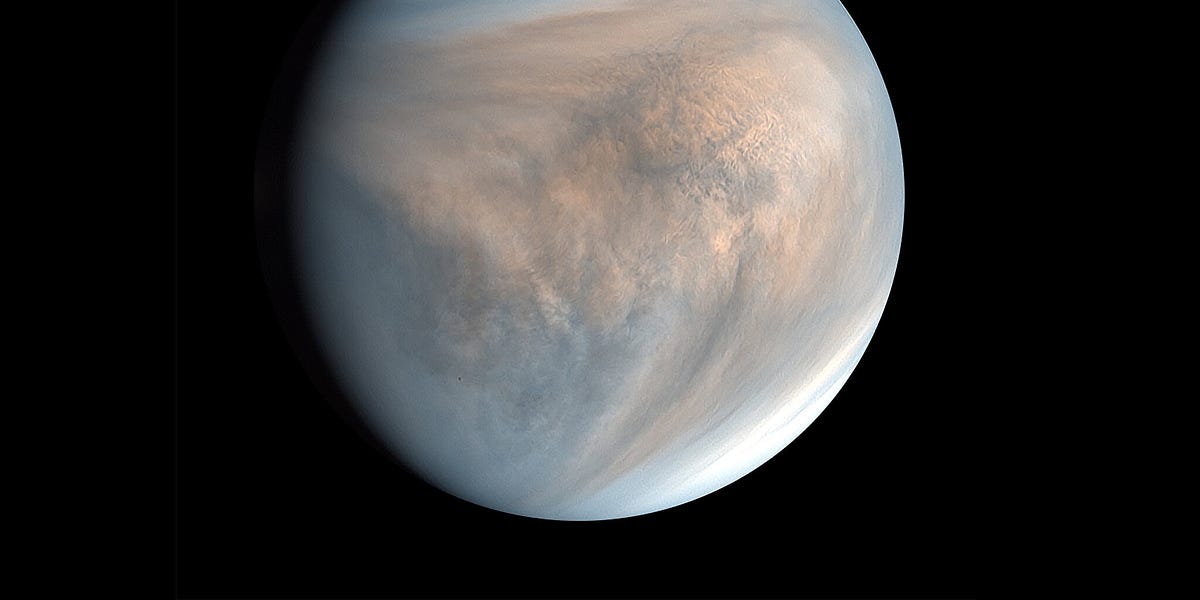

Screw the Mars hype. Here's why we should move to Venus.

Mars: The Planet that Lost an Ocean's Worth of Water
Why did Martian water evaporate into the space? Where is this vapor now? - Quora

Where Did Earth's Water Come From? Researchers Offer Exciting Explanation - Science & Health

The Red Planet: A Natural History of Mars: Morden, Ph.D. Simon: 9781639361755: : Books
Mars: the planet that lost an ocean's worth of water

Strong 'electric wind' strips planets of oceans and atmospheres